Functional MRI
Bold Technique based fMRI
MRI Biomarker for Neuronal Activities
MRI Knowledge Hub
What is Functional MRI (fMRI)
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. The fMRI concept builds on the MRI scanning technology and the discovery of properties of oxygen-rich blood. MRI brain scans use a strong, permanent, static magnetic field to align nuclei in the brain region being studied. The central thrust behind fMRI was to extend MRI to capture functional changes in the brain caused by neuronal activity. Differences in magnetic properties between arterial (oxygen-rich) and venous (oxygen-poor) blood is mapped also called Bold Imaging.
Bold Imaging in MRI uses oxygenated vs non-oxygenated blood to map the cognitive-function/neuronal activity. Task or events by human body is initiated or controlled by neuronal activity, causing spatially-specific oxygen metabolic and physiologic consequences.
In other words Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent contrast is explored in functional MRI imaging to track human brain activity called Bold imaging.
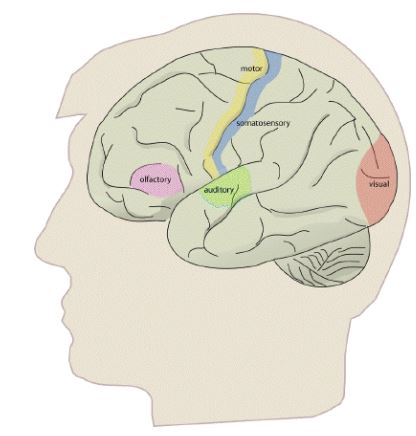
Brain Function Structure
Brain is the collection of cells, which forms nerve tissue in the anterior end of an organism. A wide variety of mental and physical processes in brain are controlled or influenced by neural activity in particular regions of the brain. In some areas of the brain, such as in the sensory or motor cortices, the organization of the brain resembles a map of the human body; this is called as the “somatotopic organization of the brain.” The brain occupies several other areas of the brain that appear to have distinct functions that are located in specific regions of the brain in most individuals. For example, areas of the occipital lobes relate to vision, regions of the left inferior frontal lobes relate to language in the majority of people, and regions of the cerebral cortex appear to be consistently involved with conscious awareness, memory, and intellect. This type of location-specific functional organization of the brain, in which discrete locations of the brain are statistically likely to control particular mental or physical functions in normal individuals, is herein referred to as the “functional organization of the brain”.
Working of fMRI
The brain function study by fMRI is done by repeatedly imaging the brain. The subject is presented with a stimulus or required to carry out some task. The fMRI process for studying brain is dependent on three aspects;
- The pulse sequence used in fMRI,
- The design of the stimulus paradigmin fMRI,
- The way the data is analysed in fMRI.
Presurgical mapping
Alzheimer’s/Dementia
Neurological deficit area
Analyzing functional/diseased area
fMRI for Cerebral Assessment Procedures


Meditation and fMRI
Functional Brain Mapping of the Relaxation Response and Meditation; Sara W Lazar, George Bush, Randy Lyanne Gollub etl.; June 2000, Neuroreport 11(7) : 1581-5
